Top 10 Natural Fat Burning Foods to Boost Your Metabolism

In our perpetual quest for a balanced lifestyle and optimal health, the role of diet cannot be overstated—especially the inclusion of natural fat-burning foods that boost metabolism and facilitate weight loss. These foods, rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber, not only aid in shedding those extra pounds but also contribute significantly to overall well-being. Incorporating elements like protein, coconut oil, and green tea into one’s diet can make a world of difference, serving as a cornerstone for anyone looking to enhance their metabolic rate and kick-start their weight loss journey.
This article will delve into a curated list of the top 10 natural fat-burning foods that are not only easy to integrate into your daily meals but are also delicious and packed with nutrients. From avocados rich in healthy fats to the metabolic-boosting properties of green coffee bean extract, each item on the list offers unique benefits, including improved digestion and enhanced energy levels. Key highlights will include the thermogenic effects of spices like cayenne pepper, the satiating power of oatmeal and chia seeds, and the surprising advantages of adding grapefruit and cinnamon to your diet. By the end of this exploration, readers will be equipped with the knowledge to harness these foods’ natural power, steering their weight loss endeavors toward success with sustainable, nourishing choices.
Top 10 Natural Fat-Burning Foods to Boost Your Metabolism
1. Avocado

Healthy Fats in Avocado
Avocados are celebrated for their high levels of monounsaturated fatty acids, crucial for maintaining healthy skin and enhancing the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients. These fats support brain health and reduce inflammation and may help lower the risk of heart disease [1][2].
Avocado Nutrition Profile
A powerhouse of nutrition, avocados provide a substantial amount of vitamins such as C, E, K, and B6, along with riboflavin, niacin, folate, pantothenic acid, magnesium, and potassium. They are also a good source of lutein, beta-carotene, and omega-3 fatty acids. Notably, avocados are rich in fiber, with about 14 grams per fruit, which aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy gut microbiome [1][3].
Creative Ways to Eat Avocado
Avocados offer versatility in culinary uses, making them a staple in many diets. They can be used in various dishes, from traditional guacamole to innovative recipes like avocado chocolate mousse or baked avocado fries. For a healthier option, avocados can replace butter in baking, adding nutrient density and a creamy texture [2]. Additionally, incorporating avocados into smoothies, salads, or as a spread on toast diversifies their use while boosting nutritional intake.
2. Grapefruit

Grapefruit and Weight Loss
Grapefruit has often been associated with weight management and is a staple in various diet plans, notably the “Grapefruit Diet,” which suggests that the fruit contains fat-burning enzymes [5]. While these claims are widely popular, scientific research provides a mixed verdict. Studies indicate that grapefruit consumption may aid in weight loss by making individuals feel fuller and thus consume fewer calories [5][6]. For instance, a study highlighted that participants who included grapefruit in their meals saw a reduction in waist size and body weight [7].
Grapefruit Consumption Tips
Incorporating grapefruit into one’s diet can be beneficial due to its high content of vitamins, particularly vitamin C, which is crucial for a healthy immune system [5]. However, it’s important to consume grapefruit wisely due to its potent interaction with certain medications. Grapefruit impacts the metabolism of various drugs, potentially leading to either increased or decreased drug efficacy [8]. Therefore, individuals on medication should consult healthcare providers about integrating grapefruit into their diets.
Grapefruit Interactions with Medications
Grapefruit and grapefruit juice can significantly affect the absorption and effectiveness of numerous medications. This interaction primarily occurs because grapefruit contains furanocoumarins, which inhibit the CYP3A4 enzyme in the small intestine, a key enzyme in drug metabolism [8]. This inhibition can lead to higher concentrations of the drug in the bloodstream, potentially increasing the risk of side effects. Commonly affected drug categories include statins, blood pressure medications, and some corticosteroids [8][9]. It is crucial for patients to check with their healthcare professionals to understand the potential risks and adjust their intake accordingly.
3. Coconut Oil

MCTs in Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is distinguished by its content of medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are fats that the body can quickly convert into energy. Unlike long-chain triglycerides found in foods like olive oil, MCTs are metabolized differently, providing a quick source of energy and potentially reducing fat accumulation in the body [10][11]. Coconut oil contains various MCTs including capric, caprylic, and lauric acid, although the inclusion of lauric acid as an MCT is controversial due to its different metabolic pathways [10].
Coconut Oil for Cooking
Renowned for its stability at high temperatures, coconut oil is a favorite in the kitchen. It can be used for baking, frying, and even as a dairy-free replacement in recipes. Coconut oil adds a rich, tropical flavor to dishes and is versatile in both savory and sweet culinary applications. From sautéing vegetables to creating decadent desserts, coconut oil’s unique properties make it a staple in diverse cooking practices [12].
Coconut Oil Health Benefits
Beyond its culinary uses, coconut oil is noted for its potential health benefits. It is a rich source of lauric acid, which has been studied for its antiviral and antibacterial properties. Some research suggests that coconut oil could play a role in reducing certain types of body fat, particularly abdominal fat. However, it’s important to note that while coconut oil may offer certain health advantages, it should be consumed in moderation due to its high-calorie content [13][11]. Studies have also explored its role in conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, where its ketone-producing ability may offer some benefits [14].
4. Chia Seeds

Chia Seeds Fiber Content
Chia seeds are a remarkable source of dietary fiber, offering about 10 grams per ounce, which constitutes approximately 35% of their weight [15]. This high fiber content is beneficial for digestive health, aiding in regular bowel movements and potentially helping to prevent conditions like obesity by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake [15][16].
Chia Seeds and Satiety
The protein and fiber in chia seeds contribute significantly to satiety, and the feeling of being full after eating. Studies have shown that incorporating small amounts of chia seeds into meals, such as mixing them with yogurt, can enhance fullness and reduce subsequent food intake, which may support weight management efforts [15]. However, it’s important to note that results regarding chia seeds’ effectiveness for weight loss are mixed, with some studies showing minimal impact [17].
Incorporating Chia Seeds in Your Diet
Chia seeds are incredibly versatile and easy to add to a variety of dishes. They can be consumed raw, soaked in juice, or added to oatmeal, puddings, smoothies, and baked goods. Their ability to absorb water and fat makes them useful for thickening sauces or as a substitute for eggs in recipes. A common serving size is about one ounce (28 grams), and it is advisable to consume them with plenty of water to aid digestion and prevent any potential gastrointestinal discomfort [15][18].
5. Green Leafy Vegetables
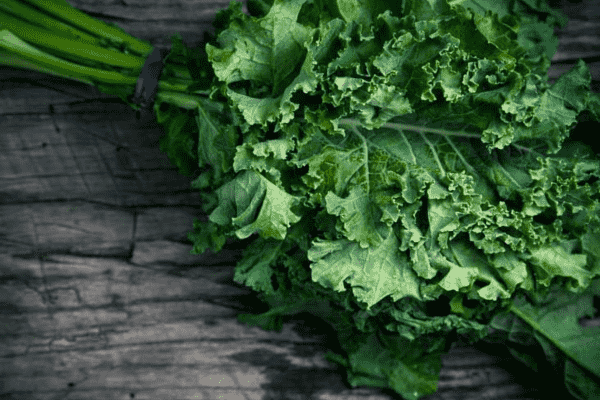

Nutrient Density of Leafy Greens
Leafy greens such as spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are celebrated for their rich content of vitamins and minerals, which are pivotal for maintaining optimal health. These vegetables are packed with vitamins A, C, K, iron, magnesium, and calcium, all essential for supporting vision, skin health, and the immune system. Additionally, the high antioxidant content in these greens is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases like cancer and heart disease [19][20]. They are also a crucial source of dietary fiber, promoting improved digestion and aiding in maintaining a healthy weight [19][20].
Best Leafy Green Options
When choosing leafy greens, options like kale, spinach, arugula, and collard greens are among the top picks due to their nutrient density. Kale, for instance, not only offers vitamins and minerals but also packs a high amount of antioxidants and fiber. Spinach is versatile and mild-tasting, making it a popular choice for a wide array of dishes. For those looking for variety, microgreens offer a concentrated source of nutrients and can be a flavorful addition to meals [20][21].
Cooking Methods for Leafy Greens
To maximize the nutritional benefits of leafy greens, certain cooking methods are recommended. Steaming is considered one of the best techniques to retain the maximum nutrients while preserving color and texture. Blanching by briefly immersing the greens in boiling water followed by a quick cool down in ice water helps retain their vibrant color and nutrients. For those who enjoy greens with a crunch, sautéing in a bit of olive oil can enhance flavors without compromising their nutritional value [22][21].
6. Whey Protein

Whey Protein and Muscle Building
Whey protein is highly regarded for its role in enhancing muscle mass and strength, particularly when paired with strength training. It contains essential amino acids that are crucial for muscle building, including a high level of leucine, which triggers muscle protein synthesis [23][24]. Studies have consistently shown that whey protein can increase muscle growth effectively when consumed around workout sessions due to its rapid absorption rate [23].
Whey Protein Shakes
As a convenient supplement, whey protein shakes are commonly consumed post-workout to aid in muscle recovery and growth. The protein in these shakes helps repair the muscles after intense exercise, promoting muscle hypertrophy and strength [25][26]. Whey protein shakes not only provide the necessary building blocks for muscle repair but also help in reducing muscle damage and inflammation, making them a favorite among athletes and fitness enthusiasts [27].
Whey Protein vs Other Protein Sources
When compared to other protein sources like soy or casein, whey protein often shows superior results in the short term for muscle gain due to its fast digestion and absorption [23]. However, casein provides a more sustained protein release, which can be beneficial for muscle growth over a longer period. Therefore, the choice between whey and other protein sources may depend on individual goals and dietary preferences [23]. Whey’s ability to stimulate muscle response quickly makes it particularly effective for post-exercise recovery and muscle maintenance [24].
8. Cinnamon
Cinnamon and Blood Sugar Control
Cinnamon has garnered attention for its potential to enhance blood sugar control. Studies suggest that cinnamon can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels by mimicking the effects of insulin and increasing glucose transport into cells [28]. It may also help manage type 2 diabetes by reducing fasting blood sugar and improving hemoglobin A1c levels, a marker of long-term blood sugar control [29][30]. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before using cinnamon as a treatment for diabetes due to mixed evidence of its effectiveness [29].
Adding Cinnamon to Your Diet
Incorporating cinnamon into the diet can be both delicious and healthful. This versatile spice can be added to various dishes, enhancing flavor while providing health benefits. Sprinkle cinnamon on oatmeal, blend it into smoothies, or add it to your coffee for a spicy twist [31]. It’s also popular in baking, where it contributes to the flavor profile of cakes, cookies, and bread. For a savory option, cinnamon can enhance the taste of stews and marinades, providing a warm, deep flavor.
Cinnamon Health Benefits
Beyond its impact on blood sugar, cinnamon is prized for its anti-inflammatory properties, which may help reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer [28]. The spice’s rich antioxidant content helps fight oxidative stress and inflammation, common factors in chronic diseases [32]. Cinnamon also exhibits antimicrobial properties, which can fight certain bacteria and fungi, potentially reducing the incidence of respiratory tract infections and improving oral health [28]. Additionally, the inclusion of cinnamon in the diet has been linked to reductions in cholesterol and triglyceride levels, further supporting cardiovascular health [28].
9. Oatmeal
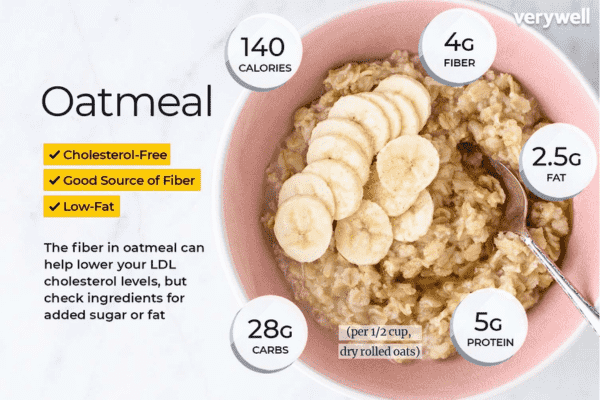
Oatmeal Fiber Content
Oatmeal is renowned for its high fiber content, particularly beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that can significantly improve cholesterol levels and heart health [33]. This fiber not only helps in reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol but also aids in stabilizing blood sugar levels by slowing digestion, which prevents spikes in blood glucose [33].
Oatmeal and Satiety
The soluble fiber in oatmeal contributes to its ability to increase satiety and reduce hunger. Studies have shown that a serving of oatmeal can enhance feelings of fullness and reduce the intake of calories in subsequent meals [34][35]. This effect is primarily attributed to the beta-glucan content, which forms a viscous gel-like substance in the gut, prolonging the feeling of fullness and helping in weight management [35].
Healthy Oatmeal Toppings
To maximize the health benefits of oatmeal, choosing the right toppings is crucial. Adding ingredients like fruits, nuts, and seeds can enhance the nutritional profile of oatmeal. For instance, berries add antioxidants, nuts provide healthy fats and proteins, and seeds like chia or flaxseed offer additional fiber and omega-3 fatty acids [36]. It’s advisable to avoid high-sugar toppings and opt for natural sweeteners like honey or maple syrup to maintain the meal’s health benefits [37].
10. Cayenne Pepper
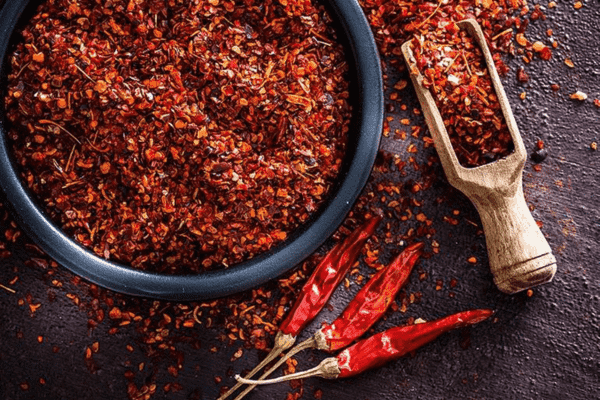

Capsaicin in Cayenne Pepper
Capsaicin, the active component in cayenne pepper, is recognized for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [38]. While it is effective in high-dose supplements, the impact of capsaicin from typical culinary amounts remains less clear, necessitating further research [38].
Cayenne Pepper and Metabolism
Cayenne pepper may boost metabolism and assist in weight management. Capsaicin is known to enhance thermogenesis—the process of heat production in organisms—which in turn could help burn calories and reduce fat [39]. Studies have shown that capsaicin can decrease appetite and increase energy expenditure, which are beneficial for weight control [40].
Using Cayenne Pepper in Cooking
Cayenne pepper can be incorporated into meals in various forms, such as fresh, dried, or powdered. It adds a spicy kick to dishes and can be used in moderation to enhance flavor without overwhelming the senses [38]. Additionally, it’s advisable to handle cayenne pepper with care to avoid irritation to the skin or eyes, and those with sensitive stomachs may need to limit their intake [38].
Green Coffee Bean Extract

Green coffee bean extract, derived from unroasted coffee beans, is rich in chlorogenic acid, a compound lost during the roasting process. This acid is known for its antioxidant properties, which can help reduce inflammation and lower blood pressure [41]. It also affects carbohydrate absorption, potentially aiding weight loss by reducing blood sugar spikes [41].
Chlorogenic Acid in Green Coffee
Chlorogenic acid, predominantly found in green coffee beans, is a natural antioxidant. It plays a significant role in managing blood pressure and has been studied for its potential in lowering blood sugar levels and supporting weight management [41][42]. This acid is also found in smaller amounts in certain fruits and vegetables, offering a broader spectrum of health benefits [43].
Green Coffee Supplements
Green coffee supplements often contain varying levels of caffeine, which can influence energy levels and metabolic rates. However, the caffeine content in these supplements can vary greatly, making it crucial to monitor intake to avoid potential side effects such as anxiety or sleep disturbances [41][44]. It’s important to consult healthcare providers before starting any new supplement regimen, especially for those with caffeine sensitivities or those taking other medications [41][44].
Green Coffee vs Regular Coffee
While both green and regular coffee beans originate from the same plant, the unroasted green coffee beans retain a higher level of chlorogenic acid compared to their roasted counterparts. Regular coffee may still contain small amounts of chlorogenic acid, but the majority is lost during roasting [42]. This makes green coffee a preferable option for those looking to maximize their intake of this beneficial compound. Despite the similarities in caffeine content, green coffee offers a distinct profile of health benefits primarily due to the presence of chlorogenic acid [42].
Conclusion
Through examining a diverse array of natural fat-burning foods, this article has provided a comprehensive guide on how to naturally enhance one’s metabolism and support weight management efforts. From the healthy fats in avocados that support overall well-being to the metabolic boost acquired from green coffee bean extract, each food item contributes uniquely to a balanced and nutritious diet. We have also explored the role of specific foods such as grapefruit, coconut oil, and chia seeds, not only for their weight loss benefits but also for their broader health advantages, including improved heart health and enhanced satiety.
The inclusion of these foods in one’s diet represents a pivotal step towards achieving a healthier lifestyle, underscored by their natural properties that aid in weight management and provide essential nutrients. As we continue to navigate the challenges of maintaining optimal health in a modern world, these carefully selected foods offer a beacon of hope and a path towards sustainable dietary habits. While further research may enhance our understanding of their full benefits, the current knowledge equips us with valuable insights to make informed nutritional choices that contribute to our overall health and well-being.
FAQs
What foods can help increase metabolism and promote fat burning?
Certain foods are known to enhance metabolism and aid in fat burning, including:
- Water: Vital for overall health and helps maintain body weight.
- Green Tea: Known to boost metabolism and accelerate fat oxidation.
- Soup: This can be filling and thus help in reducing overall calorie intake.
- Grapefruit: Helps in managing appetite and body weight.
- Apples and Pears: High in fiber, which can enhance feelings of fullness.
- Broccoli: Rich in fiber and low in calories, supporting weight management.
- Low-fat Yogurt: This can aid in digestion and fat reduction.
- Lean Meat: High in protein, which is essential for metabolism and burning fat.
Which five foods are effective at reducing belly fat?
To target belly fat, incorporating these five types of foods may be beneficial:
- Soluble Fiber: Found in fruits, vegetables, and legumes, helps reduce fat accumulation.
- Protein-rich foods: Such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy, support muscle building and fat loss.
- Fatty Fish: Like tuna and salmon, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, and known for fat-burning properties.
- Probiotic Foods: Including yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi, which enhance gut health and metabolism.
- Green Tea: Boosts metabolism and fat oxidation.
How can I quickly boost my metabolism and increase fat burning?
To enhance your metabolism and accelerate fat burning, consider these strategies:
- Regular Meals: Eating at consistent times can help maintain metabolic balance.
- Adequate Calories: Consuming enough calories prevents the body from entering a starvation mode which slows down metabolism.
- Protein in Every Meal: Helps in building muscle, which in turn boosts metabolism.
- Green Tea: Its metabolic-enhancing properties can aid in quicker fat burning.
- Weight Lifting: Builds muscle mass, inherently increasing metabolic rate.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Effective in burning fat quickly.
- Sufficient Water Intake: Essential for optimal metabolic function.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can lead to weight gain, so managing it is crucial for metabolism.
What are the top three foods known for their fat-burning capabilities?
The three potent fat-burning foods are:
- Eggs: High in protein, they help in muscle building and fat reduction.
- Nuts: Provide good fats and proteins, which are essential for a healthy metabolism.
- Oily Fish: Such as salmon, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, is known to aid in fat-burning and overall weight loss.




